biology and environment
biology and environment
biology and environment
biology and environmentStructural
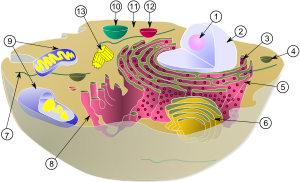
ces between cell types are particularly relevant to molecular biology.
Anatomy considers the forms of macroscopic structures such as organs and organ systems.]
Genetics is the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms. Genes encode the information necessary for synthesizing proteins, which in turn play a central role in influencing the final phenotype of the organism. In modern research, genetics provides important tools in the investigation of the function of a particular gene, or the analysis of genetic interactions. Within organisms, genetic information generally is carried in chromosomes, where it is represented in the chemical structure of particular DNA molecules.
Developmental biology studies the process by which organisms grow and develop. Originating in embryology, modern developmental biology studies the genetic control of cell growth, differentiation, and "morphogenesis," which is the process that progressively gives rise to tissues, organs, and anatomy. Model organisms for developmental biology include the round worm Caenorhabditis elegans, the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, the zebrafish Danio rerio, the mouse Mus musculus, and the weed Arabidopsis thaliana.(A model organism is a species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in that organism provide insight into the workings of other organisms.)]